Demystifying ERP System Mechanics: How They Operate
Explore the intricate mechanics behind ERP systems, from database management and deployment models to server infrastructure and robust security measures.
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern business, where efficiency & integration reign supreme, there emerges a silent orchestrator behind the scenes – the ERP system. Much like a conductor directing a symphony, an ERP system harmonizes the diverse elements of an organization into a well-coordinated masterpiece. Today in this blog we will explore key features and benefits of ERP systems, modules of ERP systems, Implementation Processes, Working Mechanisms of ERP Systems & many more. Welcome to a realm where complexity finds its equilibrium, and chaos metamorphoses into coherence – welcome to the demystification of ERP system mechanics. So Let’s Go!!!
What Is An ERP System?
An enterprise resource planning (ERP) system is a software suite that integrates all the critical factors of an organization's business operations, including accounting, manufacturing, sales & human resources. ERP systems are like an all-in-one platform for all data, which can help businesses enhance efficiency, productivity & decision-making.
More read- The Revolutionary Power of ERP System in Manufacturing Business- Why Your Business Should Make The Switch!
What are the different types of ERP systems?
There are three different types of ERP systems: On-premise, Cloud-based & Hybrid ERP systems. Let’s discuss a little bit about these-
1. On-premise ERP Systems:
On-premise ERP systems typically stay installed on the organization's servers. This type of ERP system is more secure & reliable, but on the other hand, it can be more costly to execute & maintain.
2. Cloud-based ERP Systems:
Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted in the cloud & accessed over the internet. This type of ERP system is more scalable & affordable, but it can be less secure.
3. Hybrid ERP Systems:
Hybrid ERP systems are a mixture of on-premise & cloud-based systems. This type of ERP system offers the best of both worlds, but it can be more complicated to execute & handle.
What Are The Core Components Of ERP Systems?
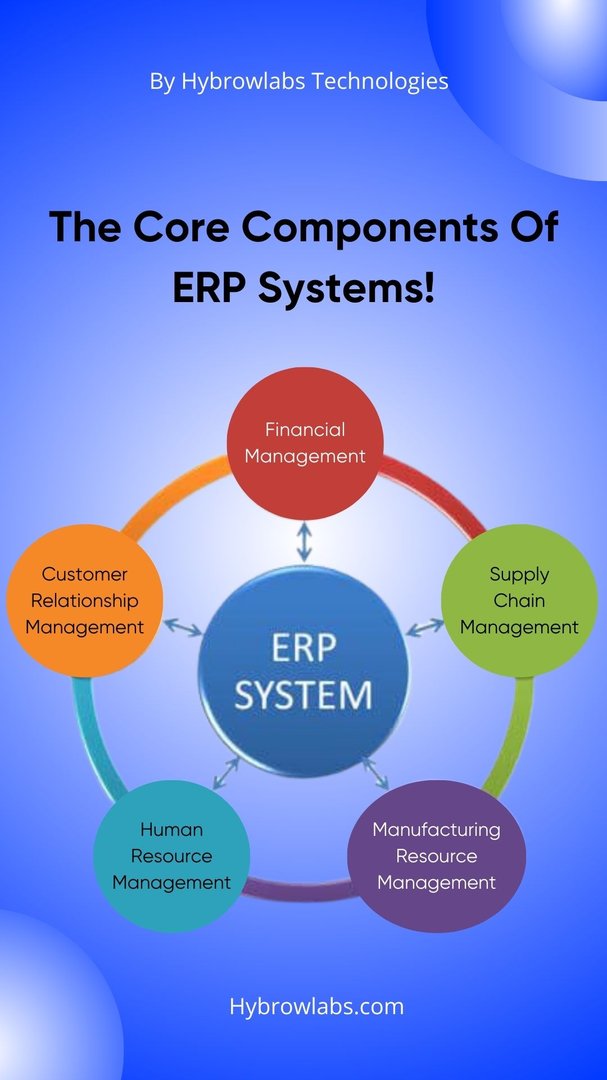
The components of an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system refer to the distinct modules or functional areas that collectively make up the comprehensive software solution. These components cover various aspects of business operations & are designed to integrate & streamline processes across different departments within an organization. Each component focuses on a specific area of functionality, enabling efficient data management, communication & decision-making. Here are some common components of ERP systems:
1. Financial Management:
The financial management module of an ERP system is responsible for tracking all of the financial transactions of a business. This includes things like accounts receivable, accounts payable, general ledger & budgeting. The financial management module helps businesses to improve their financial reporting, cash flow management & budgeting.
2. Human Resources Management:
The human resources management module of an ERP system is responsible for managing all of the human resources information for a business. This includes things like employee records, payroll, benefits & training. The human resources management module helps businesses to improve their compliance with employment laws, manage their workforce more effectively & attract and retain top talent.
3. Supply Chain Management:
The supply chain management module of an ERP system is for handling all of the activities involved in the flow of goods & services from suppliers to customers. This includes things like demand planning, inventory management, order fulfillment & transportation. The supply chain management module helps businesses to improve their efficiency, reduce costs & improve customer service.
4. Manufacturing:
The manufacturing module of an ERP system helps in managing all of the activities involved in the production of goods. This includes things like bill of materials, routing & scheduling. The manufacturing module helps businesses to improve their production efficiency, reduce costs & improve product quality.
5. Customer Relationship Management:
The customer relationship management (CRM) module of an ERP system helps in maintaining all of the interactions between a business & its customers. This contains things like sales, marketing, & customer service. The CRM module helps businesses to enhance their customer satisfaction, increase sales & build stronger relationships with their customers.
6. Inventory Management:
The inventory management module of an ERP system is responsible for tracking all of the inventory levels for a business. This includes things like raw materials, work-in-process & finished goods. The inventory management module helps businesses to improve their inventory accuracy, reduce costs & improve customer service.
Underlying Technology Infrastructures of ERP System:
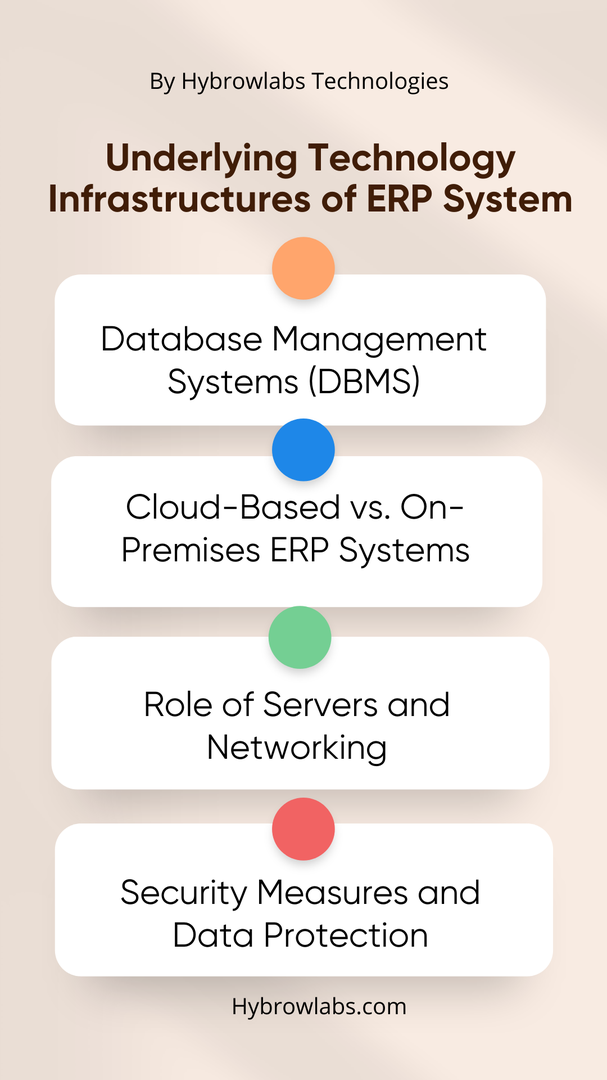
Modern business operations are increasingly reliant on the seamless integration of diverse functions & this is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come into play.
1. Database Management Systems (DBMS):
Imagine an ERP system as a digital brain that processes & stores vast amounts of data. At its core lies the Database Management System (DBMS), a crucial component responsible for organizing & retrieving data efficiently. The DBMS ensures that information is stored in a structured manner, enabling swift access when required. This structure is essential for maintaining data integrity & consistency across the various modules of an ERP system. Moreover, DBMS types, such as relational & NoSQL databases, offer different strengths, contributing to the agility & adaptability of ERP solutions.
2. Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises ERP Systems:
The deployment model of an ERP system—whether cloud-based or on-premises—significantly influences its mechanics & performance. Cloud-based ERP solutions offer unparalleled scalability, allowing businesses to expand operations without the constraints of physical infrastructure. On the other hand, on-premises ERP systems provide greater control & customization options but may require substantial maintenance & resources. The choice between these models hinges on factors like organizational size, budget, and IT capabilities & sometimes a hybrid approach combining the best of both worlds.
3. Role of Servers and Networking:
Visualize ERP systems as a network of interconnected components working harmoniously to achieve operational efficiency. Servers form the backbone of this network, handling data processing, storage & communication between different modules. Scalability & load-balancing mechanisms ensure that the system remains responsive even as transaction volumes increase. The network infrastructure facilitates seamless data exchange across departments, geographical locations & even devices, fostering collaboration & real-time decision-making. Virtualization & containerization technologies add a layer of flexibility & resource optimization to modern ERP deployments.
4. Security Measures and Data Protection:
The mechanics of an ERP system go beyond just functionality; security is paramount. Protecting sensitive data is a top priority & ERP systems employ a range of measures to ensure its safety. User access controls & authentication mechanisms safeguard against unauthorized access. Encryption—both at rest & in transit—ensures that data remains confidential, even if intercepted. Intrusion detection & prevention systems act as vigilant guards, detecting and thwarting potential cyber threats. Regular data backups & robust disaster recovery strategies are in place to mitigate the impact of unforeseen events. Moreover, compliance with data protection regulations is a fundamental aspect, influencing the system's design & operation.
The Working Mechanism of ERP Systems:
The working mechanism of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems involves an intricate interplay of processes, data integration, automation & collaboration. These systems are designed to streamline & optimize various aspects of business operations through a centralized platform. Let's delve into the core elements of how ERP systems operate:
1. Data Integration and Centralization:
ERP systems consolidate data from various departments & functions into a single, centralized database. This helps to make sure that all data is correct & up-to-date & that it can be accessed by authorized users from anywhere in the community. A centralized database also makes it easier to identify & correct data errors & track trends & patterns across the organization.
2. Automation and Streamlining Processes:
ERP systems automate routine tasks & processes like order processing, inventory management & payroll. This frees up employees to focus on more strategic tasks & it can help to improve efficiency & accuracy. ERP systems can also be used to streamline processes like the order-to-cash cycle. This can lead to further improvements in efficiency & accuracy.
3. Real-time Data Insights:
ERP systems provide real-time insights into the organization's operations through dashboards & reports. This information can be used to make better decisions, identify areas for advancement & trace progress toward goals. Real-time data insights can also help to enhance customer service, by providing employees with the information they require to quickly fix customer issues.
4. Cross-Departmental Collaboration:
ERP systems facilitate communication & collaboration between departments by providing a single source of truth for data. This can help to break down silos & improve coordination between departments. For example, if a customer places an order, the ERP system can automatically notify the warehouse, the shipping department & the accounting department. This ensures that everyone is on the same page & that the order can be processed quickly and efficiently.
How ERP Systems Mechanics Solve Problems?

ERP systems are becoming increasingly important in modern business operations for several reasons. First, they can help businesses to enhance efficiency & productivity by automating many of the manual tasks that are typically involved in running a business. Second, ERP systems can help businesses to improve their decision-making by supplying them with real-time access to data from all areas of the business. Third, ERP systems can help businesses to comply with regulations like those governing financial reporting & customer privacy.
Let's delve deeper into how ERP system mechanics address key problems & provide meaningful solutions:
1. Eliminate Supply Chain Disruptions:
Global disruptions, such as pandemics or geopolitical tensions, can severely impact supply chains. ERP systems offer real-time visibility into supply chain operations, enabling organizations to identify potential disruptions early. With integrated data, businesses can quickly shift production, source alternative suppliers & adjust inventory levels, minimizing the impact of disruptions.
2. Remote Teamwork :
The rise of remote work presents challenges in communication, collaboration & data access. ERP systems act as a virtual command center, ensuring seamless communication & remote collaboration. Cloud-based ERPs facilitate secure access to real-time data from any location, enabling teams to coordinate effectively & maintain productivity.
3. Data-Driven Decision-Making:
In an era of information overload, ERP system mechanics streamline data aggregation, analysis & visualization. By presenting key performance indicators & trends in intuitive dashboards, ERP systems empower decision-makers with actionable insights, facilitating informed & data-driven strategic choices.
4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Shifting consumer behaviors demand agile responses. ERP systems provide a 360-degree view of customer interactions, enabling personalized engagement, efficient query resolution & accurate order processing. The result is enhanced customer satisfaction & loyalty, critical for sustained success.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Evolving regulations can lead to compliance complexities. ERP systems enforce compliance by integrating regulatory requirements into processes, tracking changes & generating accurate reports. This ensures adherence to standards while minimizing risks & legal challenges.
6. Operational Efficiency:
ERP system mechanics optimize operations by automating workflows & minimizing manual intervention. This results in streamlined processes, reduced errors & improved resource utilization, driving operational efficiency even in challenging times.
Step-by-step Implementation Process ERP System:
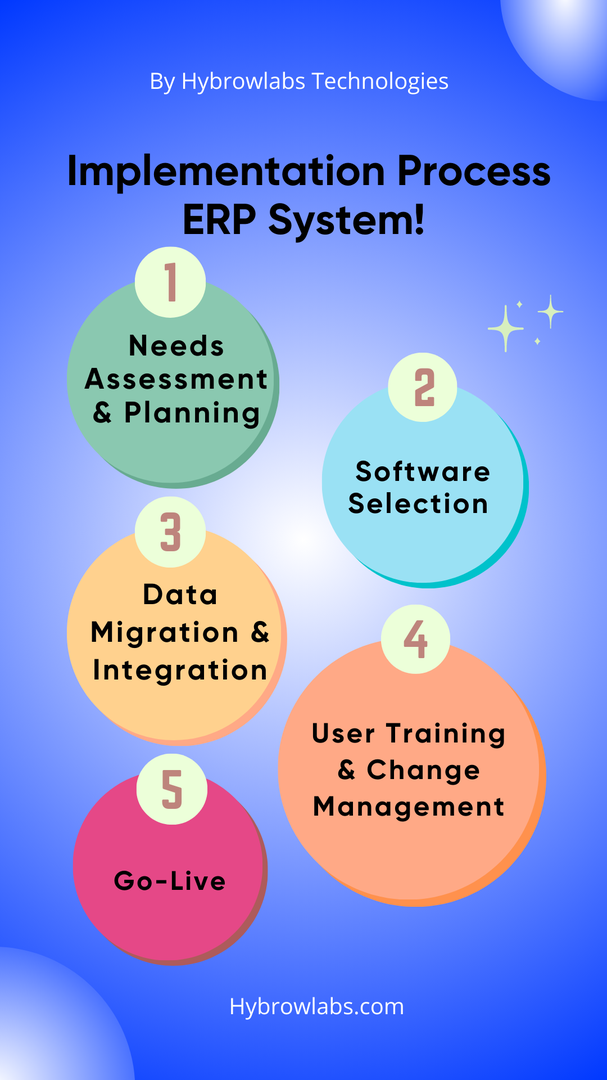
1. Needs Assessment and Planning:
The first step in the ERP implementation process is to conduct a needs assessment & develop a plan. This involves identifying the business needs that the ERP system will address, as well as setting objectives for the implementation. It is important to align the ERP strategy with the organization's overall goals.
2. Software Selection and Customization:
Once the needs assessment & plan have been completed, the next step is to choose the right ERP software vendor. There are several factors to consider when selecting an ERP software vendor. There are options like the vendor's track record, the features & functionality of the software & the level of customization. And also, it is necessary to get buy-in from all stakeholders in the organization, as the ERP system will affect everyone in the organization.
3. Data Migration and Integration:
After the selection of the software, the next step is to relocate data from the legacy systems to the new ERP system. This can be a complex & time-consuming process. Because it is important to confirm that the data is accurate & it is integrated correctly into the new system.
4. User Training and Change Management:
Once the data has been migrated, the next step is to teach employees of the organization of how to use the new ERP system. This is important to assure that the system is used effectively & that employees are capable to adopt the new system smoothly. Change management is also important during this stage because it helps to control the transition to the new system & to address any problems that employees may have.
5. Go-Live:
Once the training & change management phases have been finished, the system is ready to go live. This is the point at which the new ERP system is put into exhibit & used by the organization. It is important to observe the system closely during the go-live phase to confirm that it is working as desired & that there are no major problems.
How ERP Systems Solve the Common Challenges?
1. Data Silos:
ERP systems typically integrate data from different departments & business processes, providing a single source of truth for decision-making. For example, spreadsheets can be difficult to maintain & can lead to data silos where an ERP system can integrate data from a company's sales, marketing & finance departments, providing a unified view of the customer journey. This can help businesses to make better decisions about pricing, product development & marketing campaigns.
2. Inefficiencies in Process Coordination:
Unlike standalone tools, ERPs synchronize processes seamlessly. Consider a retailer using distinct systems for sales & inventory. A surge in demand might lead to stockouts. In contrast, an ERP coordinates sales data with inventory levels, automatically triggering restocks, thus avoiding lost sales opportunities.
3. Manual and Error-Prone Tasks:
Non-ERP setups often rely on manual interventions, prone to human errors. ERP automation minimizes such risks. Take HR functions: an organization lacking an integrated system may struggle with payroll discrepancies. ERP automates payroll, factoring in attendance & leave records, ensuring accurate & timely payments.
4. Scalability Challenges:
Scaling up demands nimble platforms. ERPs adapt effortlessly. In a software company, manual project tracking might lead to resource overload. An ERP streamlines resource allocation, scaling projects seamlessly while optimizing workloads.
You can also read- ERPNext vs Competitors: Why It Stands Out In The Crowd?
Conclusion:
The journey does not end here. The mechanism of ERP systems is a dynamic one, evolving alongside technological advancements & the changing needs of businesses. Embracing the future, these systems will likely incorporate AI, machine learning & IoT, further enriching their capabilities. If you are looking for an effective solution for your business with ERP Systems partner with Hybrowlabs & witness immense growth in your business. We have trained and expert techies who will take care of your problems & give you inner peace with more growth while you are still enjoying your vacation on a beach. Contact us & make this happen.
FAQ:
1. What exactly is an ERP system and why is it crucial for businesses?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It's a software system that integrates various business processes & functions into a centralized platform. ERP systems are essential because they streamline operations, enhance data accuracy & enable informed decision-making across an organization.
2. How does an ERP system integrate different departments within an organization?
ERP systems integrate departments by using a centralized database that stores data from various functions. This data sharing allows different departments to access & work with the same up-to-date information, promoting collaboration & efficiency.
3. How does automation work within ERP systems?
Automation in ERP systems involves creating predefined workflows & rules for routine tasks. When certain conditions are met, the system automatically triggers actions or notifications. This reduces manual effort, minimizes errors & speeds up processes.
4. Can ERP systems adapt to different industries and business sizes?
Yes, ERP systems are designed to be flexible & customizable. They can be tailored to suit the specific requirements of different industries & can be scaled to accommodate businesses of various sizes.
5. What role does real-time data play in ERP system mechanics?
Real-time data is a cornerstone of ERP systems. It provides immediate insights into key metrics & performance indicators, empowering decision-makers to make informed choices swiftly.
Sangita
Hi, thanks for taking a look at my profile. I'm Sangita, a blogger at Hybrowlabs, a web and mobile development firm. With a passion for storytelling, I create engaging content on technology, marketing, and lifestyle. My versatile writing style blends creativity with professionalism while staying up-to-date with industry trends. I aim to make complex concepts accessible and inspire through my words.
No comments yet. Login to start a new discussion Start a new discussion